That’s why it’s a good idea to keep your kernel updated as using an outdated Linux kernel could put you and your data at risk. There are a number of different ways you can go about updating the Linux kernel. The good news is that, if you mess things up, you can always boot up your system using the previous version and fix anything that went wrong. If you’re ready to say goodbye to your outdated kernel, then here’s how to complete a kernel update in Linux.
What is the Linux Kernel and Why Should You Update It?
The word kernel means the central part or core, and that’s exactly what your Linux kernel is. It’s the core of your operating system and is the link between your computer’s hardware and the applications that run on the system. Your kernel is in charge of key tasks such as managing memory and granting processes access to your CPU. In other words, it’s a pretty big deal when it comes to your computer working as expected. The strength of Linux as an operating system is that it’s open source, meaning that anyone can make improvements to the design of the software. This strength can also be a weakness, however. With changes to the software, there is a risk of vulnerabilities being created that make the OS less secure. When these vulnerabilities are discovered, patches are applied to remove them, and these patches are included in kernel updates. Keeping your kernel updated ensures that you’re keeping your system as secure as possible. A kernel update is different from a kernel upgrade. Upgrades are major moves forward in the OS, often with significant changes or new features. In contrast, a kernel update is a smaller change intended to fix minor issues with the current version. Updates are far more frequent than major kernel upgrades and don’t occur at regular intervals. That’s why it’s a good idea to regularly check for kernel updates. Alternatively, you can set up a package that can perform automatic updates for you.
How to Perform a Linux Kernel Update Using Terminal
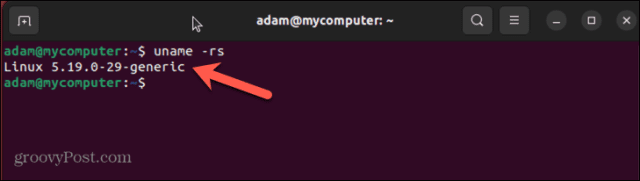
If you want to perform a manual kernel update, you can use the command line in the Linux terminal to do so. You’ll need to download the kernel that you want to install—it’s always advisable to use the latest stable kernel to avoid any unexpected problems. To perform a Linux kernel update in the Linux terminal:
How to Perform a Linux Kernel Update Using a GUI Tool
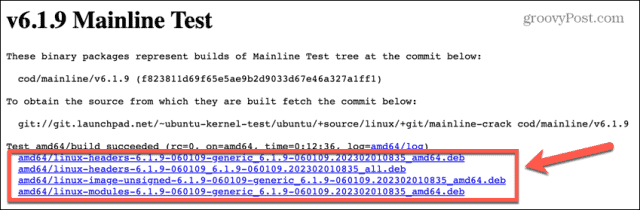
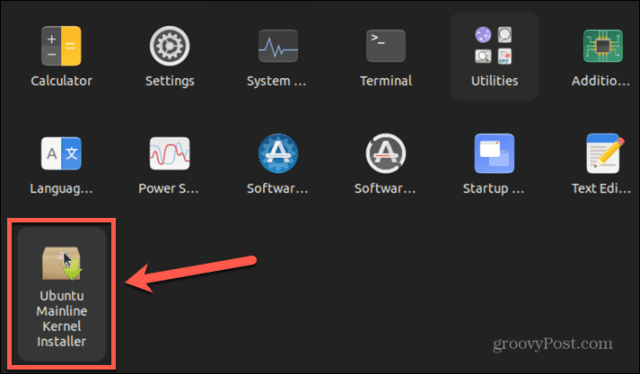
If you’re not a fan of Terminal, it’s possible to use a GUI tool to perform the Linux kernel update. One of the most popular free tools for this purpose was Ukuu, but this has now moved to a paid application. There is, however, a free fork of Ukuu called Mainline, which we will be using in this example. To perform a Linux kernel update using Mainline:
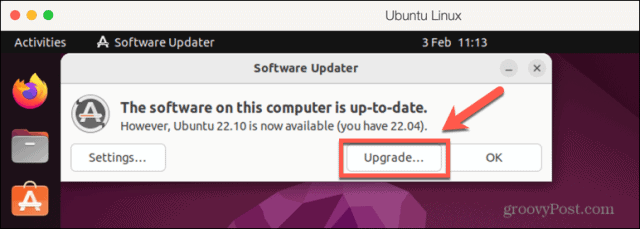
How to Perform a Linux Kernel Update Using Software Updater
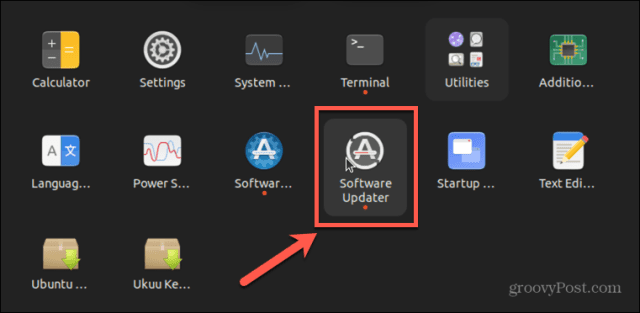
Another way to update your kernel is to update your entire OS to the latest release. The latest release is likely to include an updated version of the Linux kernel. You can usually update to the latest release through an update manager application included with your OS. In this example, we’re using Software Updater in Ubuntu. Check if this software (or similar) is available for your Linux distribution. To update your OS to the latest release using Software Updater:
Keep Linux Running Smoothly
Learning how to complete a kernel update in Linux allows you to ensure that you’re running an up-to-date version to keep your system as secure as possible. There are other things you can do to keep Linux running as smoothly as possible, however. If you find yourself running out of disk space, you can check disk space in Linux to find out what’s using it all up. When you delete those offending files, they may still not be completely gone; that’s why it’s useful to learn how to securely delete files in Linux. If you use a password for your Linux computer, and you haven’t changed yours for a while, then it could be a good idea to change your Linux password. Comment Name * Email *
Δ Save my name and email and send me emails as new comments are made to this post.
![]()